Today, keeping sensitive data safe is more important than ever. As more people store their data online, the risk of cyberattacks grows. It’s essential to make sure only authorized people can access certain information. Two great ways to do this are Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA).
In this article, we’ll explain what RBAC and MFA are, how they work, and why they are important for online security. By the end of this guide, you will understand how these methods can help protect your organization’s sensitive data.
What is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)?
Understanding RBAC
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) helps you manage who can access information based on their job role. Instead of giving permissions to each individual, RBAC assigns permissions to roles. People are then placed into these roles. This way, a person’s job determines what information they can see or edit.
RBAC helps businesses control access to sensitive data and reduces the risk of unauthorized access. It’s simple: only the people who need access to certain information can get it.
How Does RBAC Work?
In RBAC, permissions are linked to roles. When users are assigned to a role, they automatically inherit the permissions of that role. For example, an “Admin” role may have full access to all data and settings, while a “Guest” role may only be allowed to view basic information.
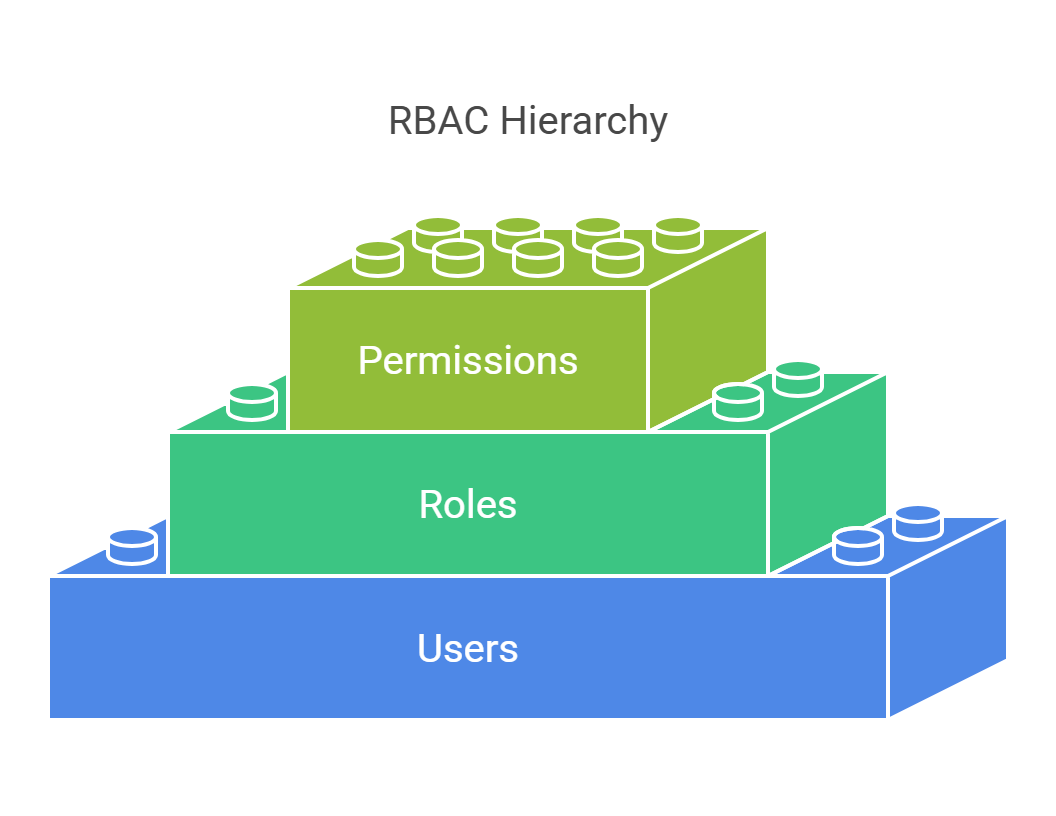
RBAC works in three ways:
-
Roles: Groups of permissions (e.g., Admin, User, Guest).
-
Permissions: The rights to do things in a system (e.g., view, create, edit, delete).
-
Users: People who are assigned to roles.
Why Is RBAC Important?
-
Reduced Risk: RBAC limits access to what’s necessary for each job. This helps keep sensitive data safe from unauthorized access.
-
Easier Management: Instead of managing permissions for each person, you only manage roles. This makes it simpler to assign and change permissions.
-
Compliance: Many industries have strict rules about who can access sensitive data. RBAC helps businesses follow these rules.
-
Scalability: As a business grows, it’s easy to add new roles and manage access without a lot of extra work.
Examples of RBAC in Action
-
Healthcare: Doctors, nurses, and administrative staff need different access levels to patient data. A doctor may have full access to medical records, while an assistant may only see appointment schedules.
-
Companies: HR staff may have access to employee records, while finance staff may only see payroll data.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
Understanding MFA
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds extra security to your accounts. It requires more than one way to verify your identity. Instead of just using a password (something you know), MFA also asks for something else, like a code sent to your phone (something you have) or your fingerprint (something you are).
MFA makes it much harder for hackers to get into your accounts, even if they have your password.
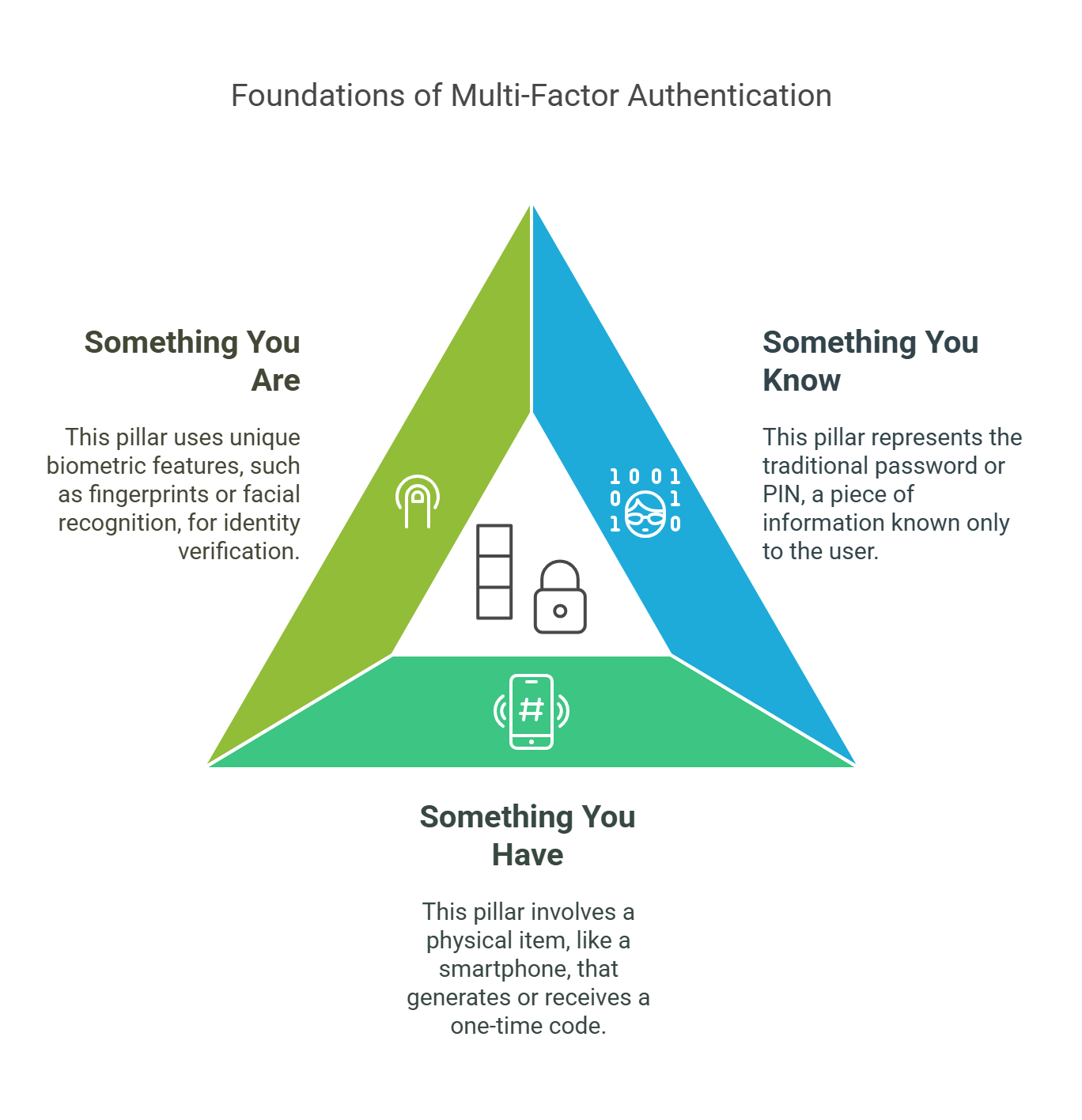
The Three Factors of Authentication
MFA usually requires three factors:
-
Something You Know: A password or PIN.
-
Something You Have: A physical item, like a smartphone, that receives or generates a one-time code.
-
Something You Are: A unique feature, such as your fingerprint or facial recognition.
These factors work together to ensure that the person trying to access the system is really who they say they are.
Why Is MFA Important?
-
Protection Against Password Theft: Even if someone steals your password, MFA requires another form of verification, so the hacker can’t get in.
-
Prevents Data Breaches: MFA adds a strong layer of security, making it harder for hackers to breach your data.
-
Compliance: Many industries require MFA to protect sensitive data. It’s a way to meet security standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
-
Builds Trust: When you use MFA, it shows customers and employees that you care about keeping their data safe.
Examples of MFA in Action
-
Banking: When you log in, you enter your password (something you know), and then you get a code on your phone (something you have) to complete the login.
-
Corporate Access: Employees use their username and password (something they know) and then confirm their identity with a fingerprint (something they are).
Combining RBAC and MFA for Extra Protection
How Do RBAC and MFA Work Together?
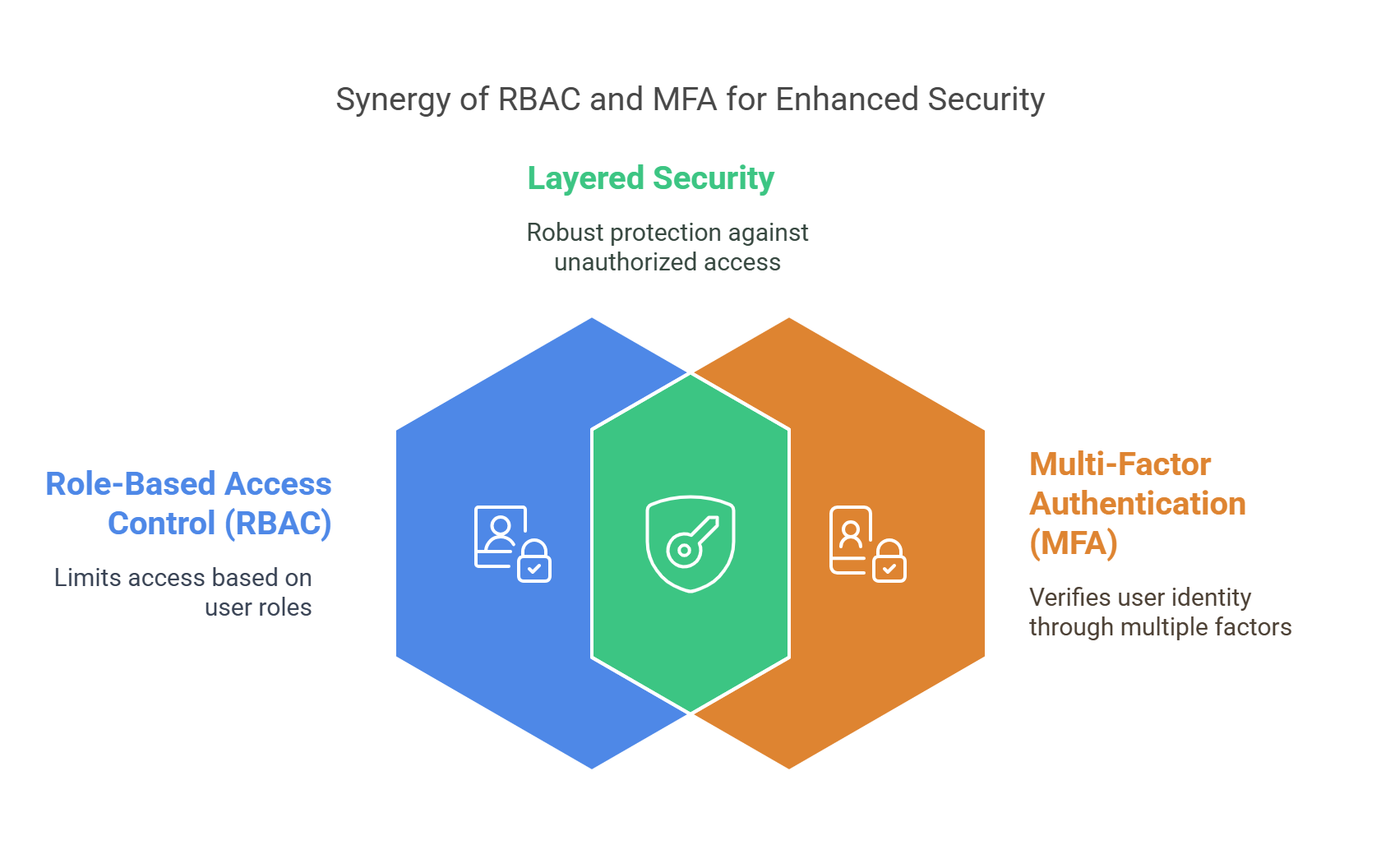
When RBAC and MFA are used together, they offer even stronger security. Here’s how:
-
Layered Security: RBAC limits access based on the user’s role, and MFA ensures that only authorized users can access sensitive information. Together, they protect data from unauthorized access.
-
Reduce Insider Threats: RBAC helps limit access, so if someone’s credentials are compromised, MFA adds an extra layer to stop hackers from getting in.
-
Prevent Mistakes: RBAC reduces the chance of accidentally exposing sensitive data by limiting access. MFA makes sure unauthorized users can’t get through, even if an error is made.
Best Practices for Using RBAC and MFA
Best Practices for RBAC
-
Define Roles Clearly: Set clear roles and only give people the access they need to do their job. Avoid giving too many permissions.
-
Review Roles Regularly: As your business grows, roles and responsibilities may change. Review and update roles to keep them accurate.
-
Use the Least Privilege: Give users only the permissions they need. This reduces the chance of data being accessed or exposed by mistake.
Best Practices for MFA
-
Use Multiple Methods: Require users to use more than one factor for authentication. For example, a password and a one-time code sent to their phone.
-
Teach Employees: Make sure your employees understand how MFA works and why it’s important. Train them to avoid common threats like phishing.
-
Use Adaptive Authentication: Some systems let you adjust the level of authentication based on the risk. For example, requiring more authentication for remote logins or unusual devices.
FAQs on RBAC and MFA
What’s the Difference Between RBAC and MFA?
RBAC controls who can access what based on job roles. MFA adds an extra step to verify a person’s identity. While RBAC controls access, MFA makes sure the right person is trying to access it.
Can RBAC and MFA Be Used Together?
Yes! RBAC and MFA work together. RBAC ensures people only have access to what they need, and MFA adds extra security to confirm their identity before allowing access.
How Does RBAC Help with Compliance?
RBAC helps businesses comply with regulations by making sure only authorized people have access to sensitive data. It also helps protect personal data as required by laws like GDPR and HIPAA.
Is MFA Foolproof?
No system is 100% secure, but MFA adds a strong extra layer of protection. It makes it much harder for hackers to get into accounts, especially when combined with other security methods like RBAC.
Conclusion: Why You Need RBAC and MFA
In today’s digital world, cyber threats are everywhere. To protect sensitive data, businesses need strong security systems like Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). RBAC makes sure people only have access to the data they need, while MFA adds extra protection by confirming the person’s identity.
Together, RBAC and MFA create a strong defense against both internal and external threats. If you haven’t already, it’s time to take action to protect your organization’s data.
Take Action Today: Start by reviewing your current access control systems and implementing MFA across your organization to strengthen your defenses and safeguard your sensitive data.


