Cloud storage is an easy and convenient way to store personal and business files. But while it offers easy access, it also introduces security risks. The good news? Encryption is a simple yet powerful way to protect your data. This guide will explain what encryption is, why it’s important, and how to use it to protect your data in the cloud.
What is Encryption for Cloud Storage?
Encryption for cloud storage is a way to keep your data safe by turning it into a format only trusted people can read. If someone gets access to your cloud storage, they won’t be able to see your files unless they have the correct decryption key.
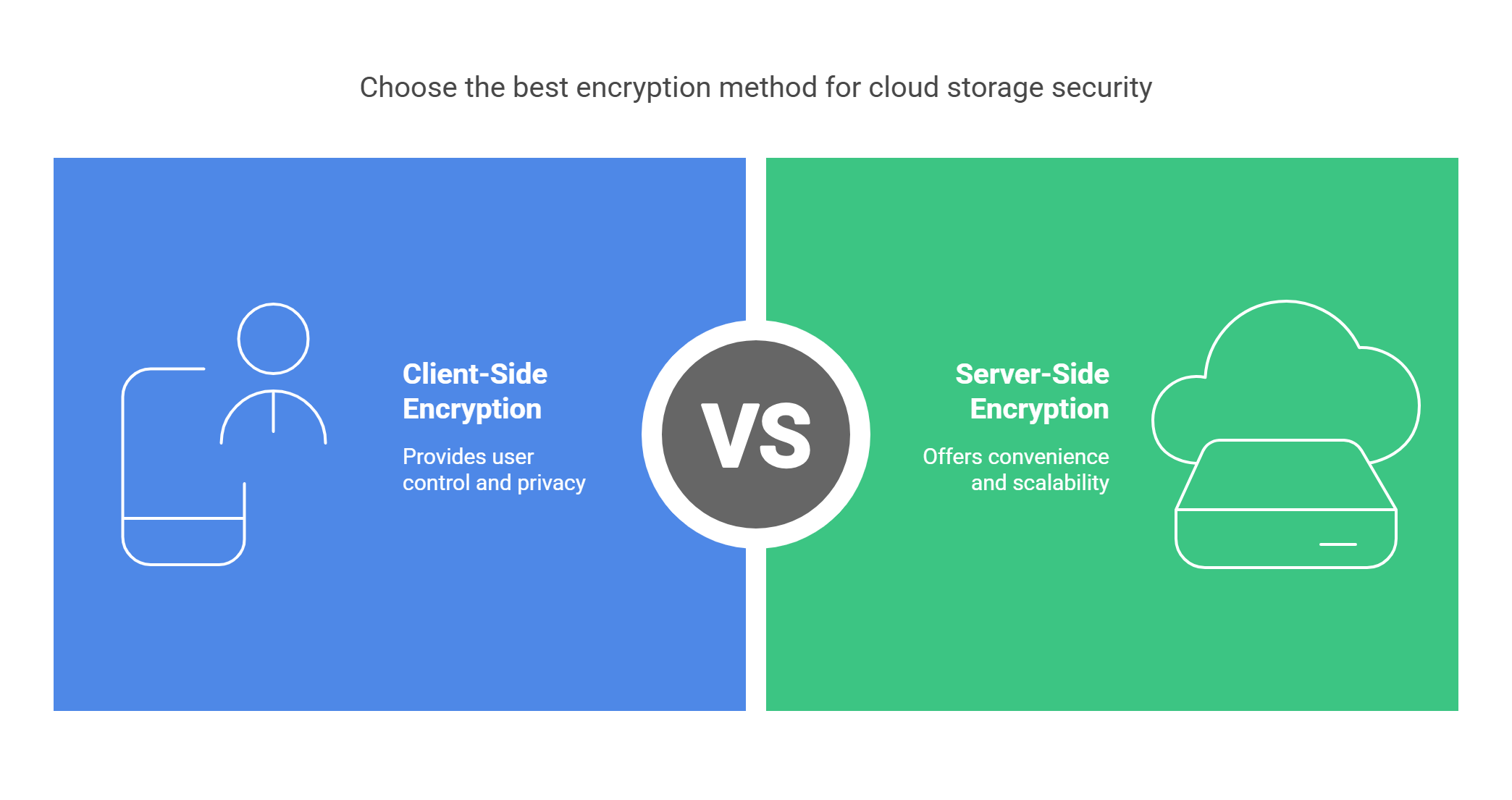
There are two main types of encryption used in cloud storage: client-side and server-side. Both protect your data, but they work differently in how and where they apply encryption.
Why is Encryption Important for Cloud Storage?
Data Protection
While cloud storage is easy to use, it can also be risky. Cybercriminals target cloud storage to steal sensitive data. Encryption helps protect your files by turning them into unreadable data unless someone has the decryption key.
Preventing Unauthorized Access
Unauthorized access is one of the biggest dangers of cloud storage. Encryption makes sure that even if someone gets into your cloud account, they can’t see or use your data.

Legal Requirements
Certain laws, like the GDPR and HIPAA, require businesses to use encryption for certain types of data. By encrypting your files, you can avoid legal problems and keep your business in compliance with data protection laws.
How Does Cloud Encryption Work?
Encryption changes data into an unreadable format. You need a key to unlock the data and turn it back to its original form.
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Encryption
-
Symmetric Encryption: This uses the same key to both encrypt and decrypt the data. Both the sender and the receiver need to have the same key.
-
Asymmetric Encryption: This uses two keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. The private key stays secret, adding extra security.
End-to-End Encryption Explained
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) means that only the sender and the receiver can access the data. Even the cloud provider can’t decrypt it because the decryption keys are only held by the user.
Types of Cloud Encryption
Server-Side Encryption
With server-side encryption, the cloud provider encrypts your data before it’s stored. This is easier, but means that the provider controls the encryption and decryption.
Client-Side Encryption
Client-side encryption means that you encrypt your data before uploading it to the cloud. This gives you more control over your data because only you have access to the encryption keys.
Benefits of Using Encryption in Cloud Storage
Increased Security
Encryption helps keep your data safe from unauthorized users, even if someone breaks into your cloud storage.
Privacy Protection
Encryption makes sure that your personal and business files remain private and protected from prying eyes.
More Control Over Data
Client-side encryption gives you full control over your data. Unlike server-side encryption, where the provider holds the decryption keys, you control your own keys.
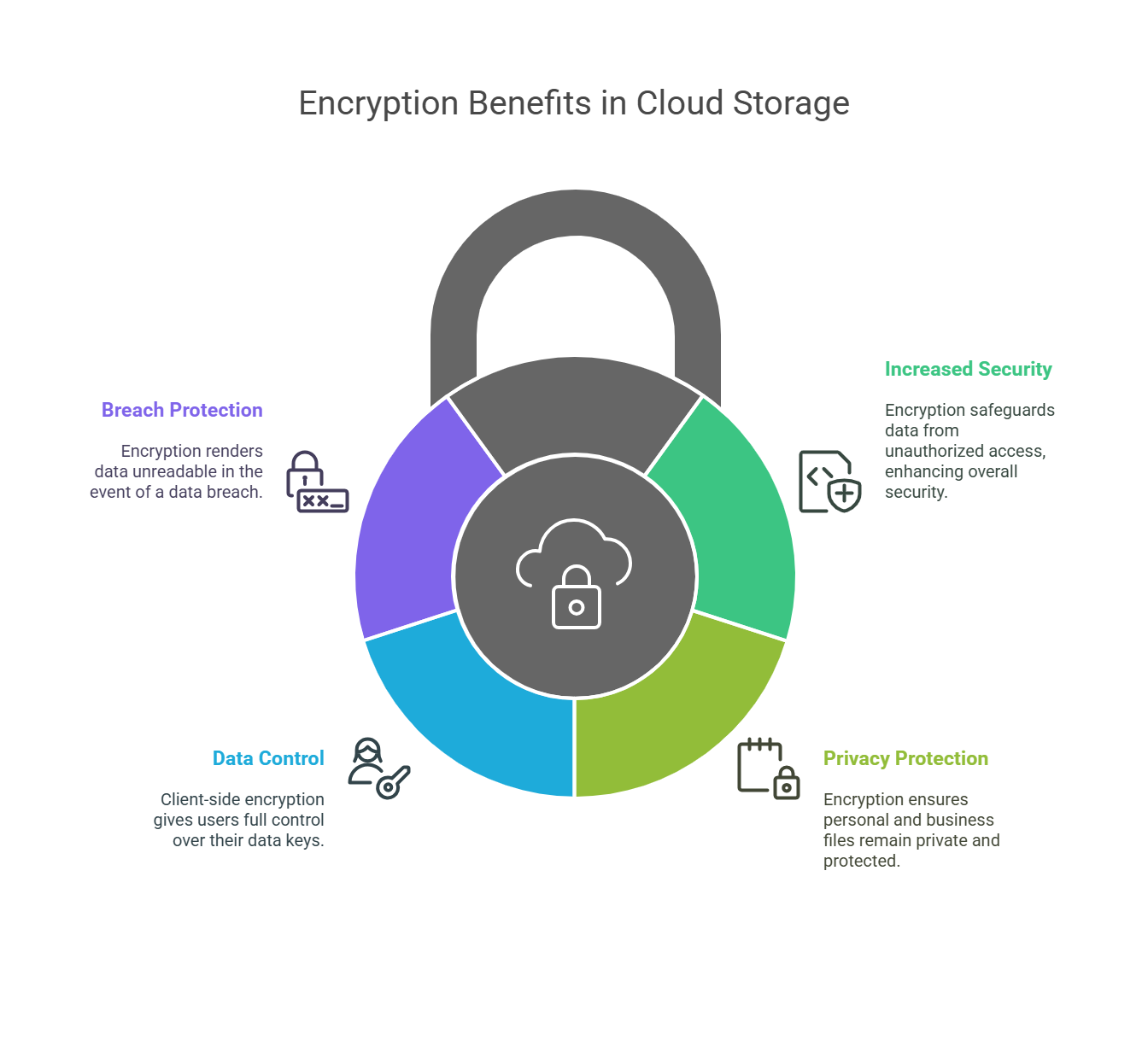
Protection from Data Breaches
If a data breach happens, encryption ensures your data is unreadable to anyone who shouldn’t have access.
Common Encryption Standards
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
AES is a secure encryption method used to protect cloud data. It’s efficient and has several key sizes, such as 128, 192, and 256 bits.
RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)
RSA is a method for encrypting data. It’s often used to securely exchange encryption keys between the sender and receiver.
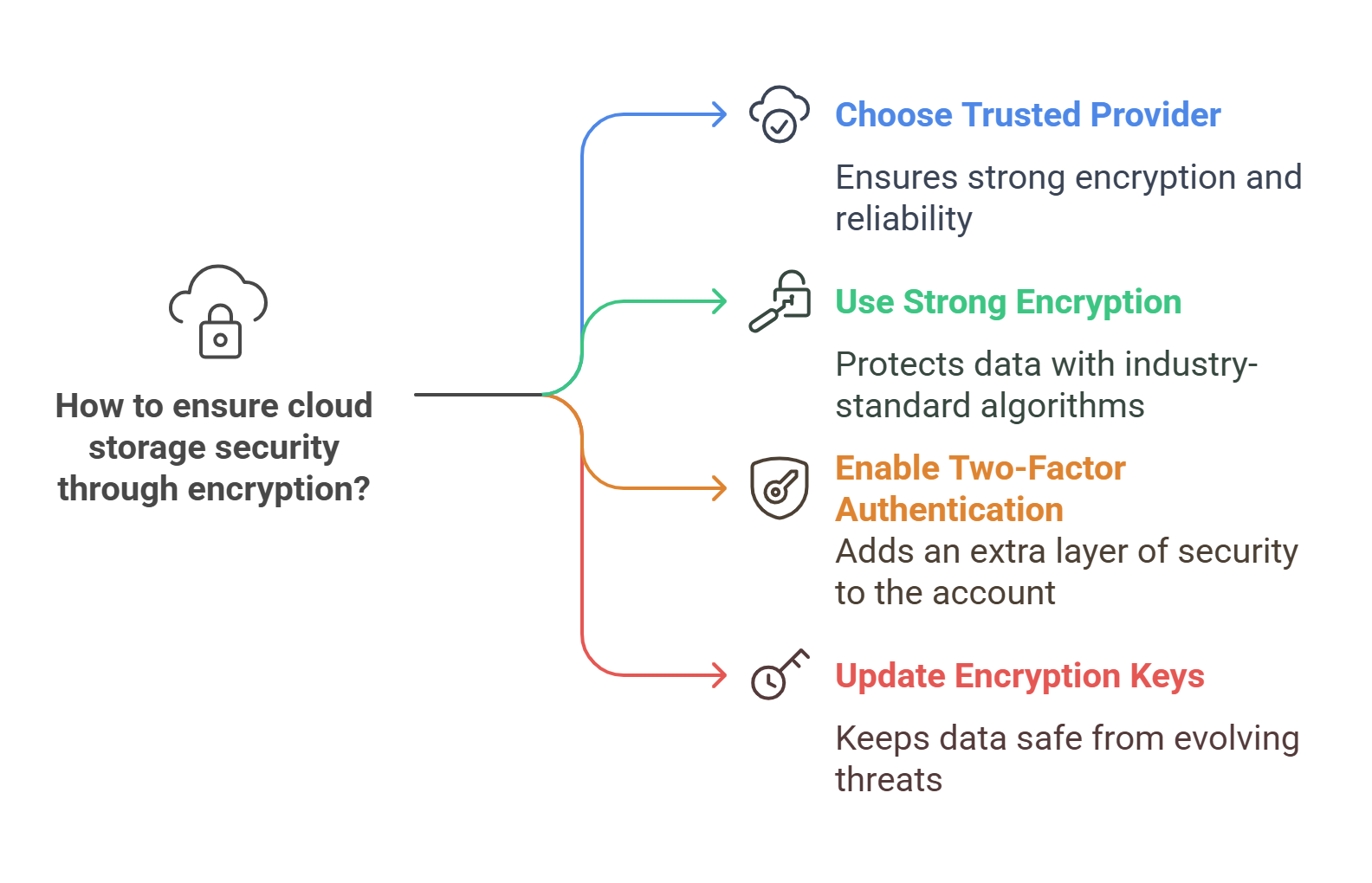
Best Practices for Cloud Storage Encryption
-
Choose a Trusted Cloud Provider: Make sure your cloud provider offers strong encryption.
-
Use Strong Encryption: Always use well-known encryption standards like AES or RSA.
-
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding another layer of security helps keep your cloud account safe.
-
Update Your Encryption Keys: Regularly change your encryption keys to stay ahead of threats.
Challenges of Cloud Storage Encryption
Key Management
Managing encryption keys can be difficult. If you lose your keys, you can’t recover your data.
Data Recovery Issues
Encrypted data is harder to recover, especially if something goes wrong. Without the correct decryption key, you may not be able to recover your files.
Performance Effects
Encryption requires extra processing power, which can slow down your system, especially when working with large files.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions about Cloud Storage Encryption
Q1: Is encryption mandatory for cloud storage?
A1: While not always required, encryption is highly recommended and sometimes mandatory depending on your data and industry.
Q2: How do I know if my cloud provider offers encryption?
A2: Look at the provider’s documentation or contact their support team for details on their encryption methods.
Q3: Can cloud providers access my encrypted data?
A3: With client-side encryption, the provider can’t access your data. With server-side encryption, they may have access to your decryption keys unless you manage them yourself.
Q4: Does encryption affect performance?
A4: Encryption can slow down performance slightly, but most providers optimize their systems to keep the impact low.
Conclusion: Is Encryption the Key to Cloud Security?
Encryption is a must for keeping your data safe in the cloud. It protects your files, ensures privacy, and helps meet legal requirements. By following best practices, you can make sure your data stays safe from unauthorized access.
Call to Action: Are you worried about your cloud storage security? Implement encryption today to protect your data from cyber threats. Choose a trusted cloud provider and take control of your data’s security.