Website security is more important than ever. With the rise of cyber threats, website owners must take steps to protect their visitors’ data, build trust, and improve SEO. One of the best ways to secure your website is by using SSL/TLS encryption. But what exactly are SSL and TLS, and why should you care? In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about SSL/TLS for websites, how it works, and why it’s essential for your online presence.
What Is SSL/TLS?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are security protocols used to protect communication between a website and its users. These protocols encrypt data sent over the internet, making it impossible for hackers to access or alter it.
The SSL/TLS Protocol Explained
SSL was the first protocol created for securing online communication, but it has now been replaced by TLS. TLS is more secure and provides better encryption. Even though TLS is now the standard, people often still refer to both SSL and TLS as SSL.
SSL/TLS works by using encryption keys to protect the data being sent between a server and the user’s browser. This ensures that sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, and personal data remains safe.
How Does SSL/TLS Work?
SSL/TLS functions through a process known as the SSL handshake. Here’s how it works:
-
Client Request: When you visit a website, your browser sends a request to the server to establish a secure connection.
-
Server Response: The server sends its SSL/TLS certificate, which contains the website’s identity and public key.
-
Validation: The browser checks the certificate’s validity. If the certificate is valid, the connection continues.
-
Session Keys: Both the server and the browser create session keys, which they use to encrypt and decrypt the data.
-
Secure Communication: After the handshake is complete, all data exchanged is securely encrypted.
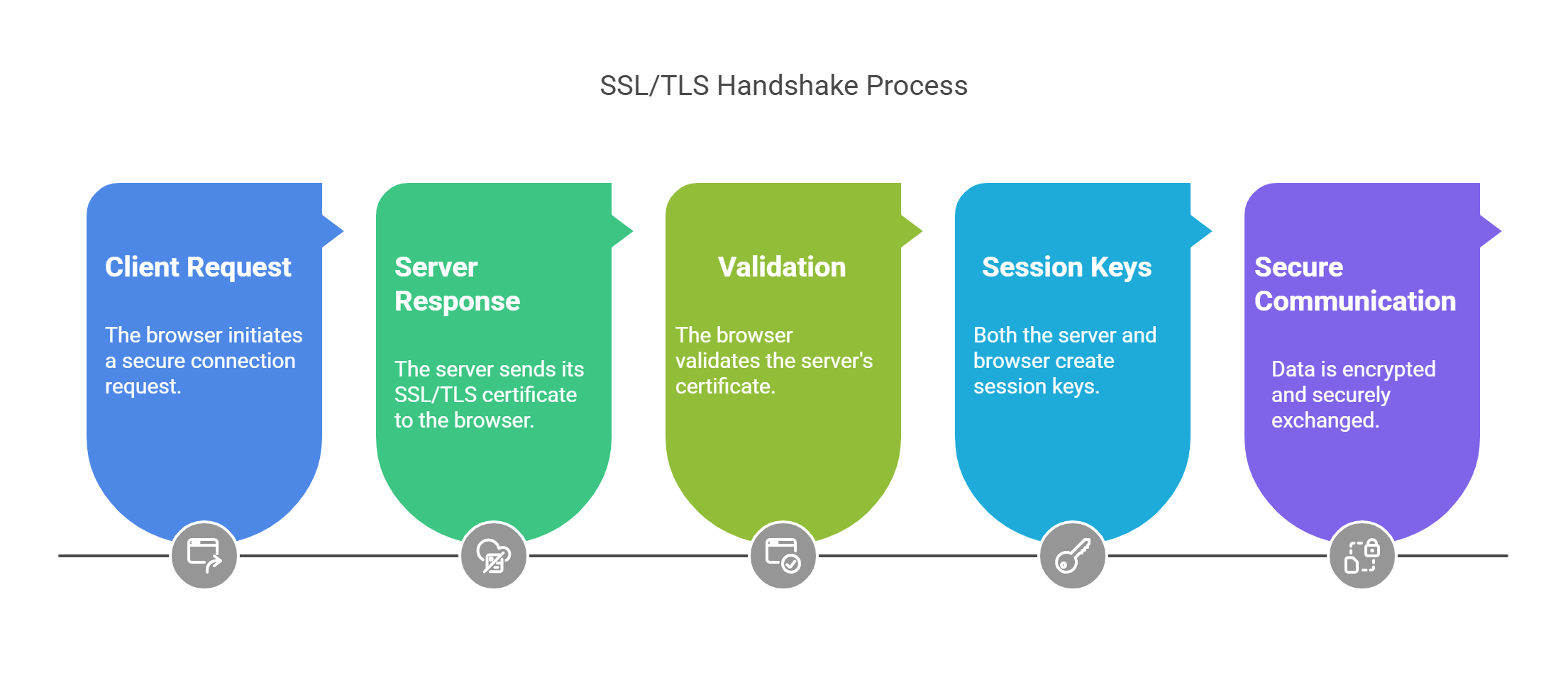
SSL/TLS ensures that no one can access or change the data while it’s being sent.
Why Do Websites Need SSL/TLS?
SSL/TLS is crucial for many reasons. Let’s go over the main ones:
3.1 Protecting User Data
SSL/TLS is essential for keeping your users’ data safe. It encrypts everything exchanged between your website and your visitors, including sensitive details like credit card information, login credentials, and personal data.
3.2 Building Trust
When a website uses SSL/TLS, it shows users that their data is protected. The padlock icon in the address bar and the “https://” prefix inform visitors that they can trust your site. Without SSL/TLS, modern browsers will label your site as “Not Secure,” which could drive visitors away.
3.3 SEO Benefits
Google ranks SSL-secured websites higher in search results. Websites with SSL/TLS encryption are more likely to rank better than those without it. Google encourages the use of SSL/TLS, meaning that securing your website can lead to more traffic and higher conversions.
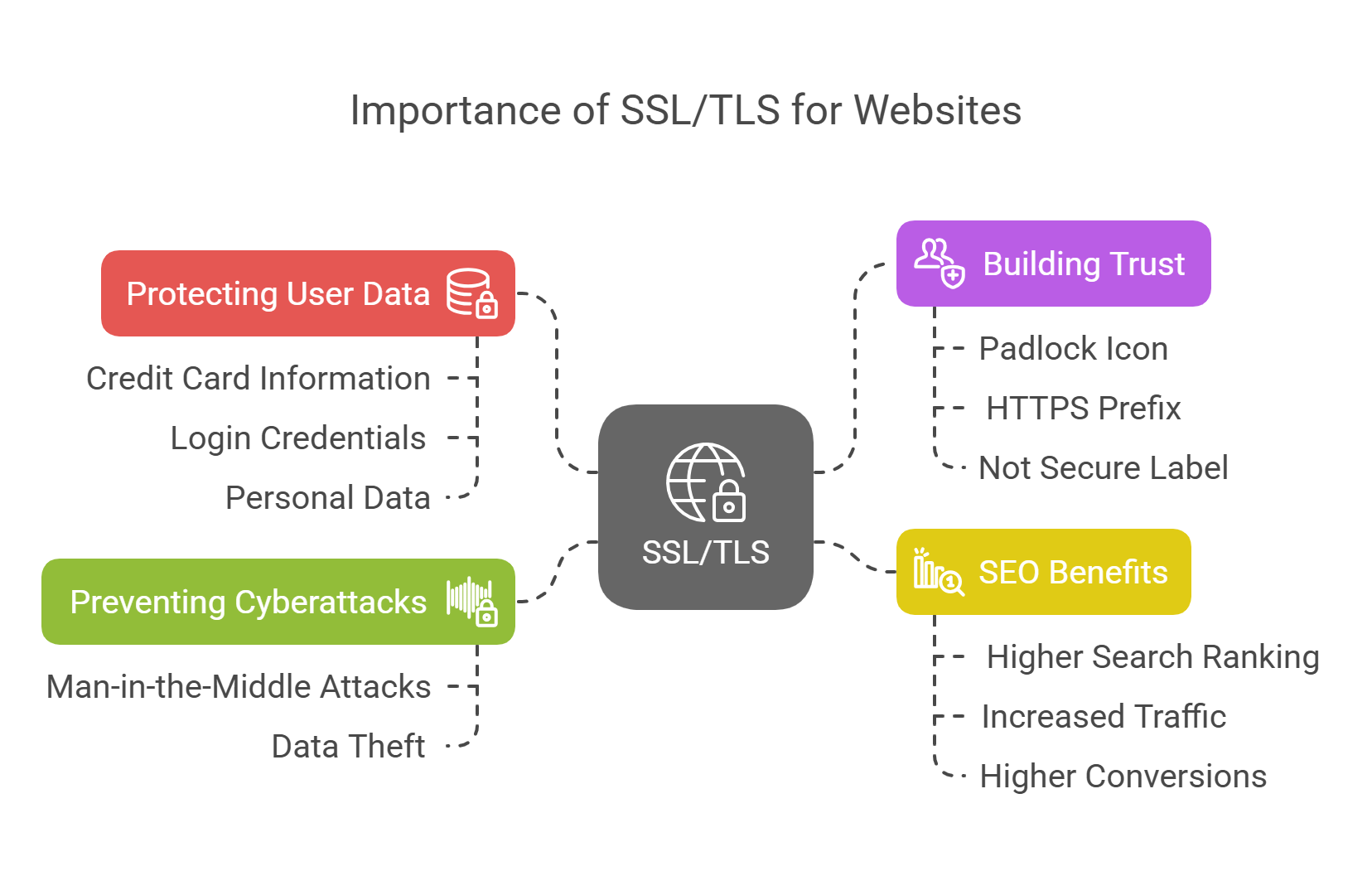
3.4 Preventing Cyberattacks
SSL/TLS helps protect against cyberattacks, such as man-in-the-middle attacks, where hackers intercept data exchanged between the server and the user. Without SSL/TLS, attackers can steal sensitive data. SSL/TLS prevents these attacks, ensuring that all data remains secure.
How to Get SSL/TLS for Your Website
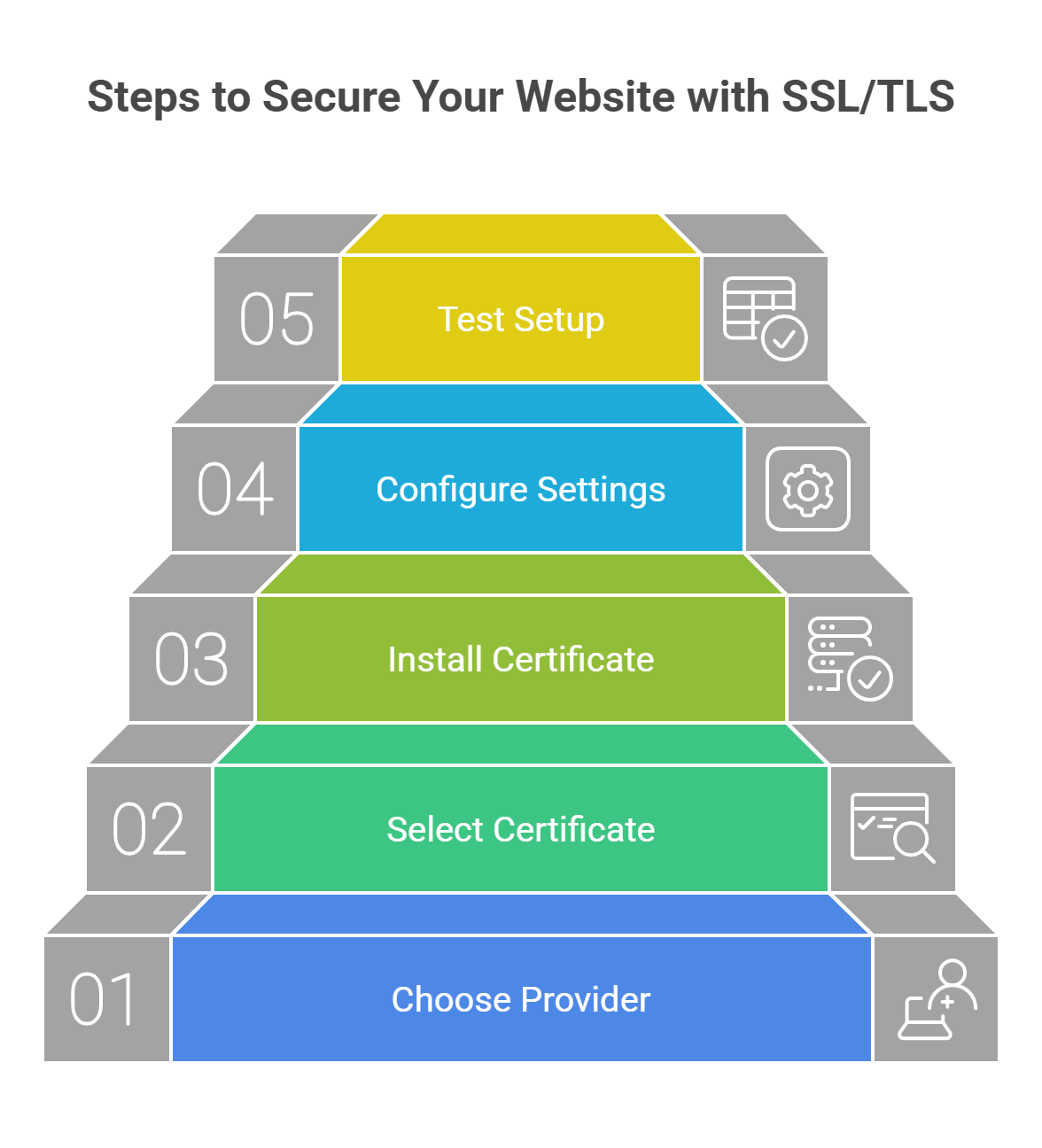
Getting SSL/TLS for your website is simple and can be done in a few steps:
-
Choose an SSL Certificate Provider: Providers like Let’s Encrypt (free), Comodo, and Symantec offer SSL certificates. Choose one that fits your needs.
-
Select the Type of SSL Certificate: Different SSL certificates are available, depending on the level of security you need.
-
Install the SSL Certificate: After obtaining your SSL certificate, install it on your server. Many hosting providers offer free SSL certificates and handle installation automatically.
-
Configure SSL Settings: Ensure that your website forces HTTPS on all pages after installing the SSL certificate.
-
Test Your SSL/TLS Setup: Use tools like SSL Labs to test your SSL configuration and make sure everything is working correctly.
SSL vs TLS: What’s the Difference?
SSL and TLS are often used together, but they’re not the same. SSL is older, while TLS is newer and more secure. TLS offers better encryption and stronger protection against vulnerabilities.
Although SSL is outdated, the term “SSL” is still often used to describe secure connections, even though TLS is the active protocol.
Types of SSL Certificates
There are several types of SSL certificates based on your website’s needs. Here are the most common ones:
-
Domain Validation (DV): The simplest SSL certificate. It only verifies that the domain owner controls the website.
-
Organization Validation (OV): A more secure certificate that verifies the organization behind the website.
-
Extended Validation (EV): The highest level of SSL certificate, requiring detailed verification. EV certificates are typically used by large corporations and financial institutions.
-
Wildcard SSL Certificates: These secure a domain and its subdomains (e.g., www.example.com and blog.example.com).
-
Multi-Domain SSL Certificates (SAN): These allow you to secure multiple domains with one SSL certificate.
Common SSL/TLS Errors and How to Fix Them
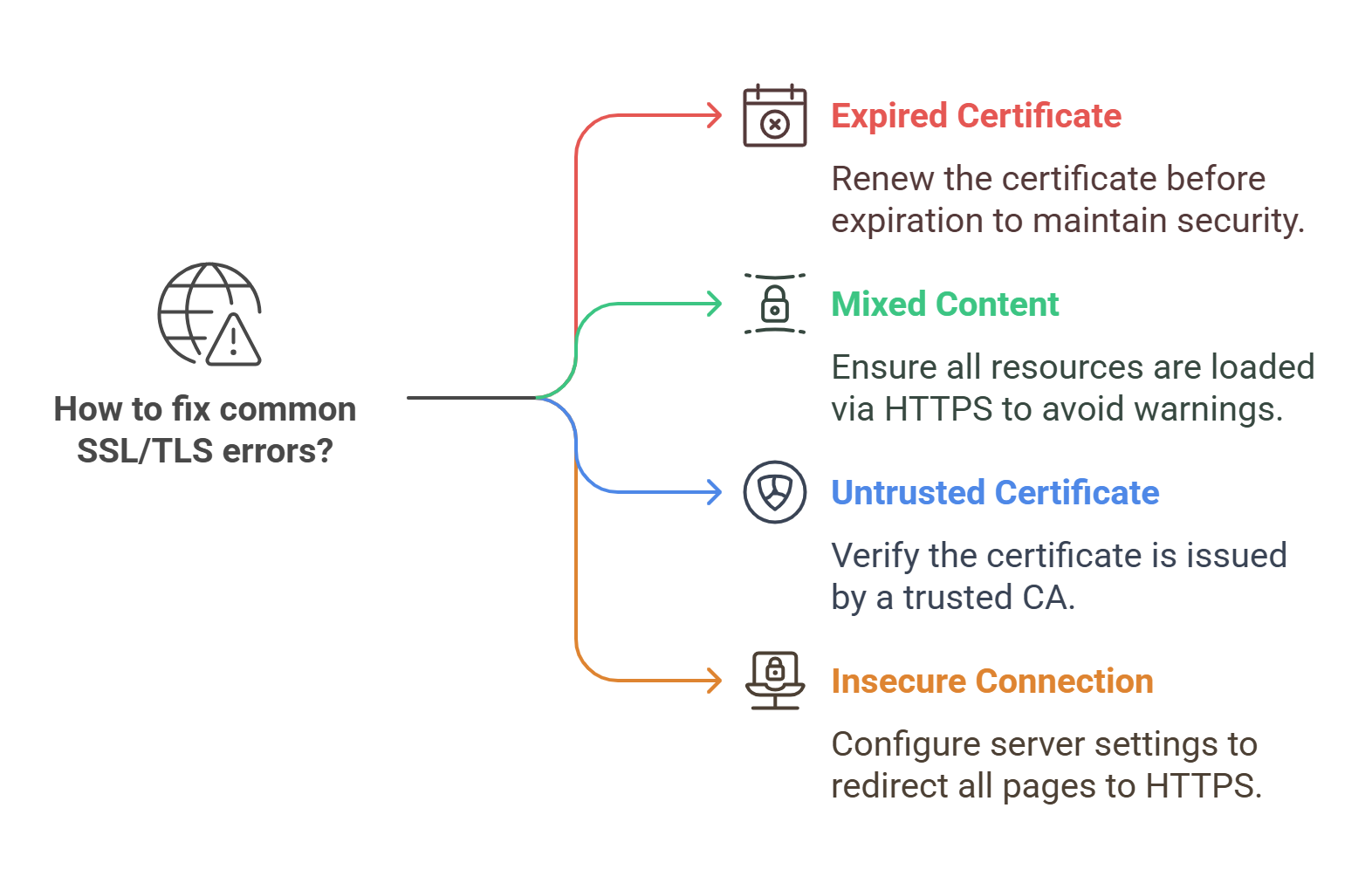
Even with SSL/TLS, some issues can arise. Here are some common SSL/TLS errors and how to fix them:
-
SSL Certificate Expired: Always keep track of your certificate’s expiration date and renew it before it expires.
-
Mixed Content Warning: Ensure that all resources (such as images and scripts) are loaded using HTTPS, not HTTP.
-
SSL Certificate Not Trusted: Make sure your certificate is issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA).
-
Insecure Connection: Double-check your server settings to ensure SSL/TLS is correctly configured and all pages redirect to HTTPS.
FAQs:
Q1: Is SSL necessary for all websites?
Yes, SSL is recommended for all websites, especially those that handle sensitive data like payments or personal information.
Q2: Can SSL improve my website’s SEO?
Yes, Google ranks SSL-secured websites higher, improving visibility and traffic.
Q3: How can I check if my website has SSL?
Look for the padlock icon in the browser’s address bar or check if the website starts with “https://.”
Conclusion: Secure Your Website Today
SSL/TLS encryption is essential for securing your website and building trust with visitors. It protects their data, improves your SEO, and prevents cyberattacks. By implementing SSL/TLS, you enhance your site’s security, credibility, and performance.
Don’t wait! Secure your website with SSL/TLS today and enjoy a safer, more trusted online presence.


