What Is Malware?
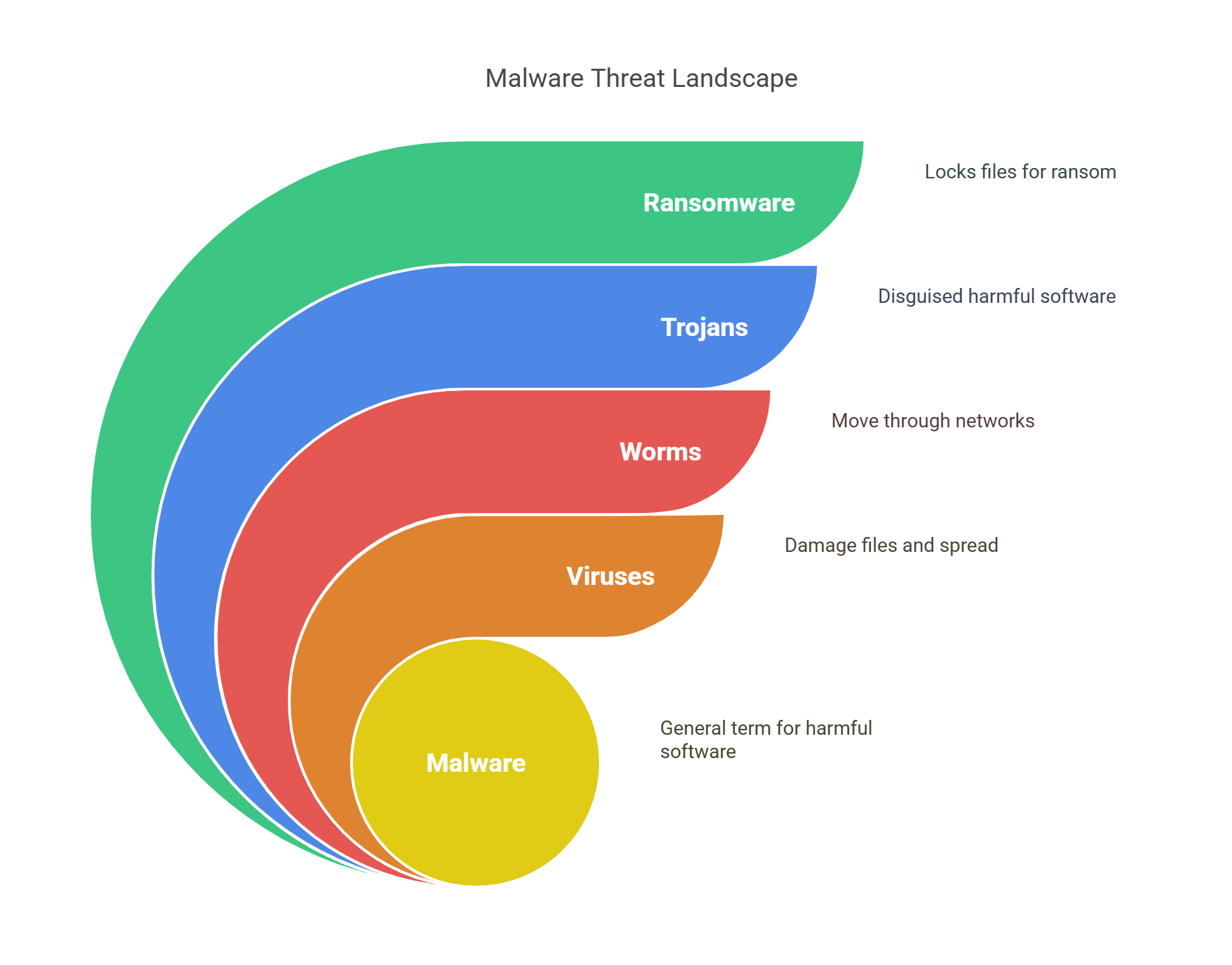
Malware means “bad software.” It harms your computer or phone. Types include:
-
Viruses: Spread and damage files.
-
Worms: Move through networks.
-
Trojans: Pretend to be safe but are harmful.
-
Ransomware: Locks your files and asks for money.
-
Spyware: Watches what you do.
-
Adware: Shows unwanted ads.
-
Keyloggers: Record what you type.
-
Rootkits: Hide deep in your system.
How Does Malware Spread?
Malware can get into your device by:
-
Opening strange email attachments.
-
Visiting unsafe websites.
-
Using infected USB drives.
-
Downloading fake apps.
-
Sharing files from unknown sources.
Once inside, it can steal data, lock files, or take control of your device.
What Is Antivirus Software?
Antivirus software finds and removes harmful programs. It looks for known threats and stops them.
How It Works:
-
Signature Scanning: Checks files against a list of bad ones.
-
Heuristic Checks: Looks for unusual behavior.
-
Sandboxing: Runs suspicious files in a safe space.
-
Real-Time Scanning: Watches for threats all the time.
Think of it as a guard checking every file you open.
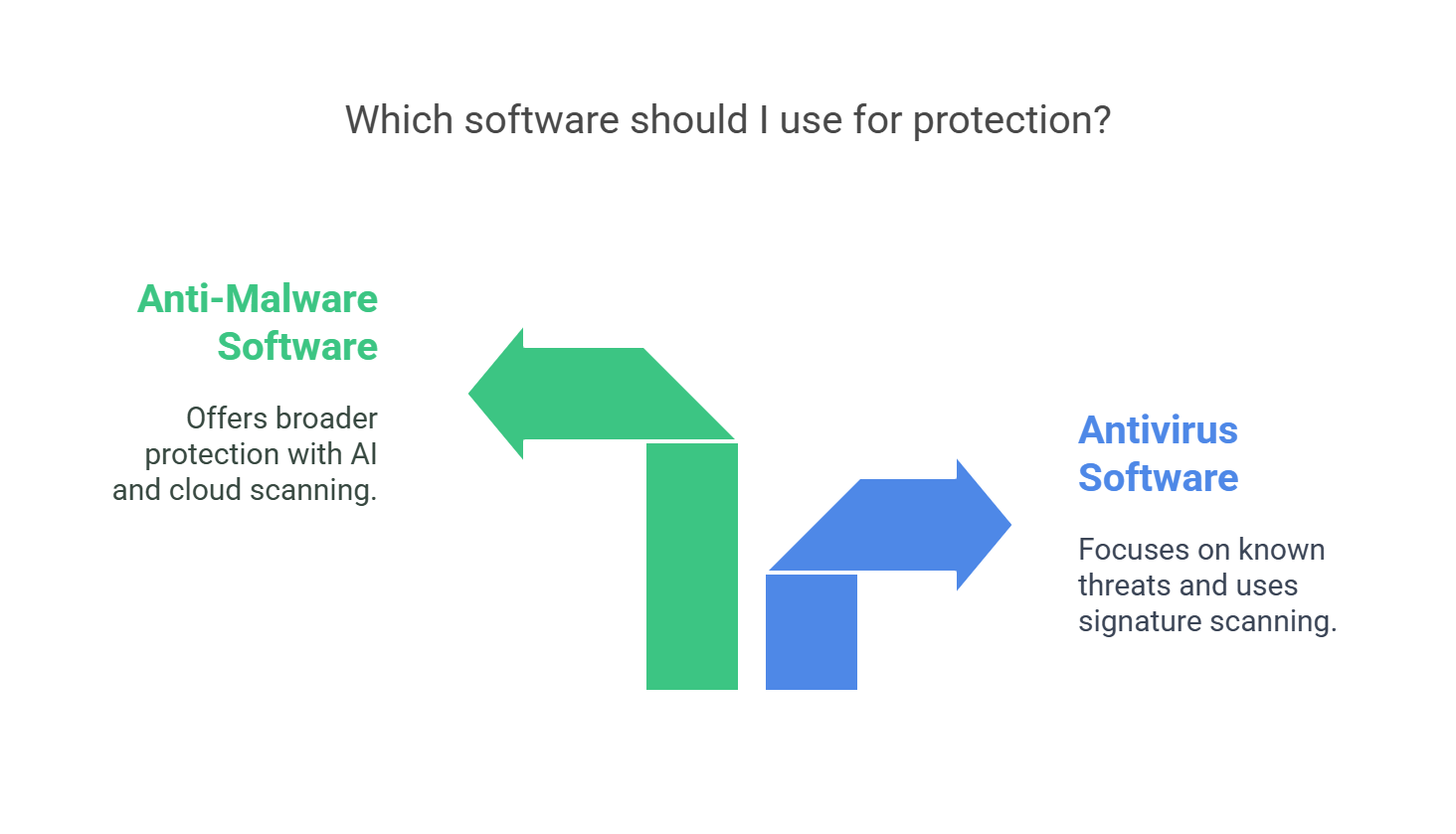
What Is Anti-Malware Software?
Anti-malware tools fight all kinds of bad software, not just viruses. They use smart ways to find new threats.
Key Features:
-
Advanced Detection: Uses AI to spot dangers.
-
Behavior Watch: Monitors apps for strange actions.
-
Cloud Scanning: Checks files using online tools.
-
Zero-Day Protection: Guards against new attacks.
-
Ransomware Shield: Stops file-locking threats.
Anti-malware includes antivirus features but does more.
Antivirus vs. Anti-Malware
| Feature | Antivirus | Anti-Malware |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Known viruses | All malware types |
| Technology | Signature-based | Behavior-based |
| Speed | Fast | May be slower |
| Threat Coverage | Old threats | New and old threats |
| Best For | Basic protection | Advanced protection |
Bottom Line: Antivirus handles common threats. Anti-malware tackles advanced ones.
Why Use Both?
Using both gives you better safety:
-
Layered Defense: Stops many types of attacks.
-
Covers Gaps: Finds threats one tool might miss.
-
Real-Time Protection: Catches problems quickly.
Together, they keep your devices safer.
Choosing the Right Security Software
Consider:
-
Compatibility: Works with your device.
-
Real-Time Protection: Always on guard.
-
Resource Usage: Doesn’t slow your device.
-
Updates: Regularly gets new threat info.
-
Support: Help when you need it.
-
Ease of Use: Simple to operate.
Trusted Security Tools
| Name | Type | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Bitdefender | Antivirus + Anti-malware | All-around protection |
| Malwarebytes | Anti-malware | Ransomware and spyware |
| Norton 360 | Antivirus Suite | Families and smart devices |
| Kaspersky | Antivirus | High detection rates |
| Windows Defender | Built-in Antivirus | Basic free protection |
How Often to Scan Your Devices
| Device Type | Scan Type | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Laptop | Full | Weekly |
| Smartphone | Quick | Daily |
| Office PC | Full | Twice a week |
| Shared Devices | Full | After each use |
Set up automatic scans to stay protected.
Are Free Antivirus Tools Enough?
Pros:
-
Free to use.
-
Basic protection.
-
Often pre-installed.
Cons:
-
Fewer features.
-
May miss new threats.
-
Limited support.
Free tools are a start, but paid versions offer better security.
Real-Life Malware Examples
-
WannaCry Ransomware: Cost businesses over $4 billion.
-
Pegasus Spyware: Stole data from phones secretly.
-
Adware: Slows devices and shows unwanted ads.
-
Keyloggers: Steal passwords and personal info.
Malware can cause big problems in real life.
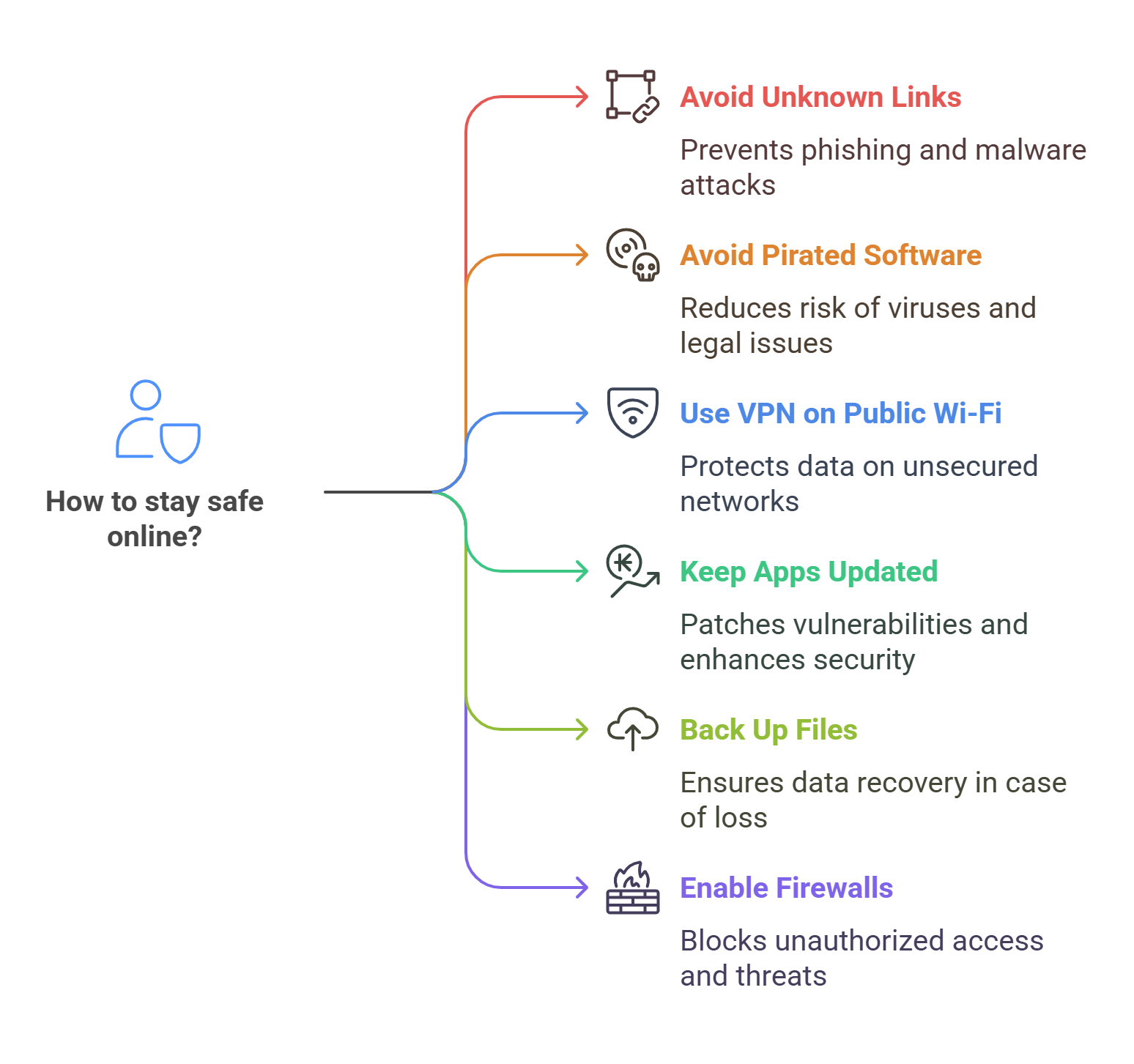
Tips to Stay Safe
-
Don’t click on unknown links or attachments.
-
Avoid downloading pirated software.
-
Use a VPN on public Wi-Fi.
-
Keep apps and systems updated.
-
Back up important files regularly.
-
Enable firewalls and spam filters.
FAQs
Q: What’s the difference between a virus and malware?
A: A virus is a type of malware that spreads to other files. Malware includes all harmful software.
Q: Can I use antivirus and anti-malware together?
A: Yes. Using both gives better protection.
Q: Are Macs safe from malware?
A: No. Macs can also get malware.
Q: Does antivirus work without the internet?
A: Basic features may work offline, but updates need the internet.
Q: Will anti-malware slow my device?
A: Some may. Choose lightweight options for better speed.
Cost of a Cyber Attack Example
Imagine ransomware locks your business systems for three days:
-
Downtime Cost per Day: $5,000
-
Ransom Demanded: $2,000
-
Data Recovery Cost: $3,000
Total Estimated Cost: $5,000 x 3 + $2,000 + $3,000 = $20,000
Investing in a $50/year antivirus plan could save you from this loss.
Final Thoughts
Cyber threats are growing. Basic defenses aren’t enough. Using both antivirus and anti-malware tools is smart and simple.
Next Steps:
-
Download trusted tools like Malwarebytes or Bitdefender.
-
Schedule regular scans.
-
Teach your family or team about online safety.
-
Back up your files often.
Stay safe online by taking these easy steps.